Skin conditions slideshow
Use this slideshow to recognise common skin conditions, including eczema, psoriasis, ringworm and vitiligo, and find out more about treatments.
Visit the 'skin conditions slideshow' on NHS Choices.Warts
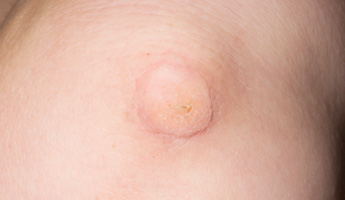
Common warts (verruca vulgaris) are firm and raised with a rough surface that can look a bit like a cauliflower. They can occur anywhere but are most common on the hands (knuckles and fingers), elbows and knees. Warts vary in size from 1mm to more than 1cm. They are caused by your body being infected with a virus called the human papilloma virus (HPV). Most warts clear up without treatment. However, the time it takes for a wart to disappear will vary from person to person.
More on wartsUrticaria or hives
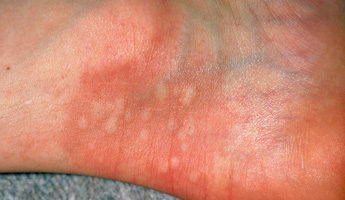
Urticaria (also known as nettle rash, hives or welts) is a raised, red, itchy rash that appears on the skin. Urticaria happens when a trigger causes an allergic reaction. The trigger could be a certain food or a sting from a nettle, bee or wasp. It causes the body to release a protein called histamine. Histamine causes tiny blood vessels, called capillaries, to leak fluid. The fluid collects in our skin and causes a rash. The rash normally disappears after a few days, but some cases can last longer. It isn't contagious.
More on urticaria or hivesRingworm
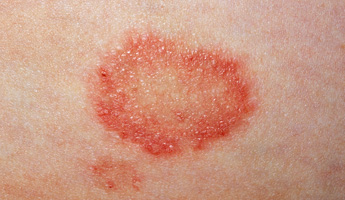
Ringworm is identifiable by the appearance of a ring-like rash on the skin. The skin will be red and inflamed around the rim but healthy inside the ring. The ring may multiply and grow, and rings can also merge together. The rings will feel slightly raised to the touch and the skin under the rash may be itchy. Most cases of ringworm are mild and can be treated using over-the-counter antifungal medication. Serious complications, such as permanent hair loss or scarring, are rare.
More on ringwormVerrucas
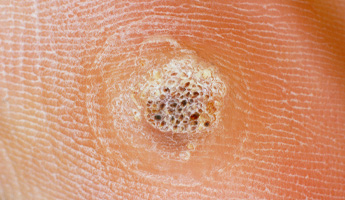
Verrucas (plantar warts) are warts that occur on the soles of your feet, heels or toes. Verrucas do not stick up from the surface of the skin. They often have a black dot in the centre surrounded by a hard, white area. The weight of your body pushing down on them makes them grow back into your skin, which can be painful. Most verrucas clear up without treatment. However, the time it takes for a verruca to disappear will vary from person to person.
More on verrucasPsoriasis
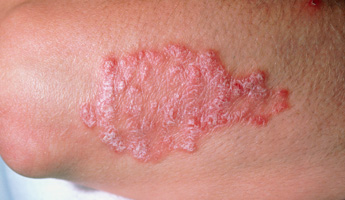
Psoriasis is a skin condition in which skin cells reproduce too quickly. It can start at any age, but most often develops in adults under the age of 35. The symptoms are dry, red lesions (known as plaques) which are covered in silver scales. They normally appear on the elbows, knees, scalp and lower back, but can occur anywhere on the body. The plaques are normally itchy, sore or both. In severe cases, the skin around your joints may crack and bleed. Psoriasis is not contagious and most people are affected only on small patches of their body.
More on psoriasisPityriasis rosea
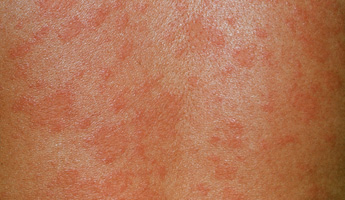
Pityriasis rosea is a rash of scaly, pink plaques. It is thought to be caused by a viral infection, but is not contagious. Before the rash starts, an initial patch of red, scaly skin appears, usually on your chest or back. This is known as the ”herald patch”. The red, circular herald patch is usually about 2-5cm across. It fades to pink after a while and reveals an outer ring of scaling. Several days later, the skin breaks out into a secondary rash of smaller (1-2cm), oval scaly patches. Pityriasis rosea is harmless and goes away without treatment.
More on pityriasis roseaHerpes cold sores
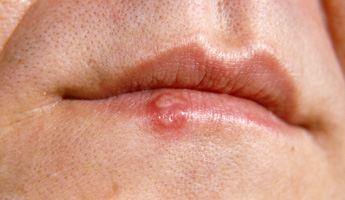
Cold sores are small, blister-like lesions that usually appear around the mouth. They are caused by the herpes simplex virus. Cold sores usually clear up without treatment in 7-10 days. Creams are available over the counter to ease the symptoms of cold sores. The triggers that cause cold sores vary from person to person. Some people have cold sores that recur frequently (two or three times a year, for example), while others only ever have one.
More on herpes cold soresVitiligo
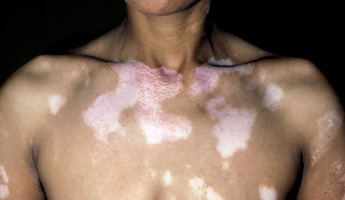
Vitiligo is a chronic condition that causes pale, white patches on the skin. The areas affected have little or no melanin (a pigment that gives skin its colour). Vitiligo can affect any area of your skin, but is most common on skin that is exposed to the sun, such as on your face, neck and hands. The symptoms of vitiligo vary from person to person. The main symptoms are flat, white spots or patches on your skin. There is no way to predict how much of your skin will be affected, and the white patches are usually permanent.
More on vitiligoAcne
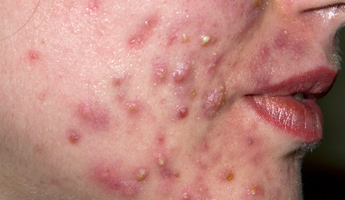
Acne is a chronic skin condition that affects most people at some point. It causes spots on the skin, usually on the face, back and chest. Symptoms can be mild, moderate or severe. Acne is thought to be caused by changes in hormones that are triggered during puberty. In girls, most acne occurs between the ages of 14 and 17, and in boys between the ages of 16 and 19. Treatments for acne include creams, gels or antibiotics, depending on how severe it is. Treatment can take two to three months to work.
More on acneAthlete's foot
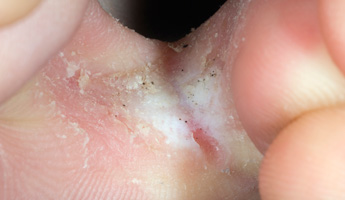
Athlete's foot is a common condition. It is caused by a fungal infection that affects the skin on your feet. The infection is normally mild and is easy to treat. Athlete's foot causes you to develop a rash, usually in the spaces between your toes. The rash can cause your skin to be itchy, scaly, flaky, dry and red. Most cases of athlete's foot can be treated using some self-care techniques and an antifungal treatment.
More on athlete’s footNon-bullous impetigo
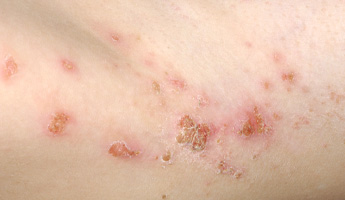
Impetigo is a highly contagious bacterial infection of the skin. The symptoms begin with the appearance of red sores, usually around the nose and mouth. The sores quickly burst, leaving thick, golden crusts. Sores are not painful but may be itchy. Other symptoms of infection, such as fever and swollen glands, are rare but may occur in more severe cases. Antibiotic cream or oral antibiotics are usually required to treat the condition.
More on non-bullous impetigoAtopic eczema
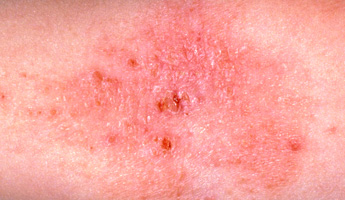
Eczema is a chronic skin condition that causes the skin to become itchy, reddened, dry and cracked. Eczema usually develops in the creases of your skin, such as the front of your elbows, behind your knees, the front of your ankles, around your neck or around your eyes. During a flare-up, atopic eczema can cause the skin to become extremely itchy, red, hot, dry and scaly. It may also be weeping and swollen. Although there is no simple cure for atopic eczema, the symptoms of an eczema flare-up can usually be eased with a variety of treatments.
More on atopic eczemaContact dermatitis
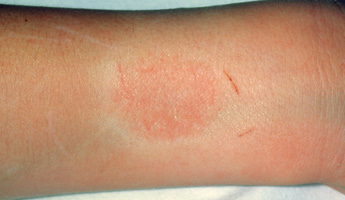
Contact dermatitis occurs when your body comes into contact with an allergen that causes your skin to become inflamed, red, blistered, dry, thickened or cracked. An allergen is a substance that causes your immune system (which normally fights illness and infection) to react abnormally. It may take several hours or days for symptoms to appear. When you're exposed to an allergen for the first time, you become sensitised to it. After that, every time you have contact with it, it causes a reaction. With treatment, symptoms of contact dermatitis can be effectively managed.
More on contact dermatitisVisit the skin conditions slideshow on NHS Choices.
NHS Choices 2014